Only released in EOL distros:
Package Summary
scriptable_monitoring
- Maintainer: Igor Makhtes <igor AT cogniteam DOT com>
- Author: Igor Makhtes <igor AT cogniteam DOT com>
- License: MIT
- Source: git https://github.com/cogniteam/scriptable_monitoring.git (branch: master)
The node manages script addition, removal and execution. It also provides an information retrieval interface for available scripts and some useful details about each script.
Example script
Suppose we have a node that publishes current CPU usage to the /cpu topic. Each message contains an array named cores with usage information for each core. We also have a topic with configuration information: /config.
Now we will create a simple script which will warn about high cpu usage.
Predicate
1 #! type predicate
2 #! name cpu_monitor
3 #! interval 1
4 #! hardware_id lab_pc_1
5 #! fail warn
6 core1 = {/cpu/cores[0:1]}
7 core2 = {/cpu/cores[1:2]}
8 core3 = {/cpu/cores[2:3]}
9 core4 = {/cpu/cores[3:4]}
10 cpu_th = {/config/cpu_threshold}
11 core_th = {/config/core_threshold}
12 average = (core1 + core2 + core3 + core4) / 4.0
13 average < cpu_th
14 core1 < core_th
15 core2 < core_th
16 core3 < core_th
17 core4 < core_th
Python
1 #! name cpu_monitor
2 #! interval 1
3 #! hardware_id lab_pc_1
4 #! fail warn
5 core1 = topic("/cpu/cores[0:1]")
6 core2 = topic("/cpu/cores[1:2]")
7 core3 = topic("/cpu/cores[2:3]")
8 core4 = topic("/cpu/cores[3:4]")
9 cpu_th = topic("/config/cpu_threshold")
10 core_th = topic("/config/core_threshold")
11 average = (core1 + core2 + core3 + core4) / 4.0
12 validate.is_true(average < cpu_th, "Cpu usage too high")
13 validate.is_true(core1 < core_th, "core1 usage too high")
14 validate.is_true(core2 < core_th, "core2 usage too high")
15 validate.is_true(core3 < core_th, "core3 usage too high")
16 validate.is_true(core4 < core_th, "core4 usage too high")
You can activate the script using rqt plugin - http://wiki.ros.org/scriptable_monitor_rqt
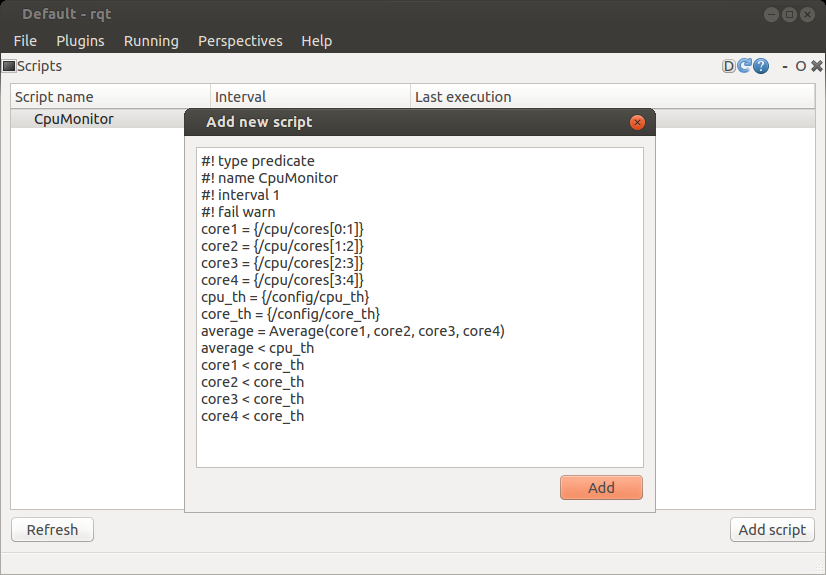
Documentation
Scripts
Configuration parameters
Parameters are preceded by '#!'. Syntax:
#! parameter_name parameter_value
There is one required parameter: "name" - the identification name of the script, it must be unique.
Example:
#! name cpu_monitor
