Show EOL distros:
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Repository: pr2-ros-pkg
- Source: hg https://kforge.ros.org/pr2mechanism/hg
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: hg https://kforge.ros.org/pr2mechanism/hg (branch: pr2_mechanism-1.5)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: hg https://kforge.ros.org/pr2mechanism/hg (branch: default)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: hg https://kforge.ros.org/pr2mechanism/hg (branch: default)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: Austin Hendrix <ahendrix AT willowgarage DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/PR2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: hydro-devel)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: Devon Ash <dash AT clearpathrobotics DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/pr2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: indigo-devel)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers insidecontroller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: Devon Ash <dash AT clearpathrobotics DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: unmaintained
- Maintainer: ROS Orphaned Package Maintainers <ros-orphaned-packages AT googlegroups DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/pr2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: kinetic-devel)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: unmaintained
- Maintainer: ROS Orphaned Package Maintainers <ros-orphaned-packages AT googlegroups DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/pr2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: kinetic-devel)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: unmaintained
- Maintainer: ROS Orphaned Package Maintainers <ros-orphaned-packages AT googlegroups DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/pr2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: melodic-devel)
Package Summary
This package contains the robot model that is used by the realtime controllers inside controller manager. This robot model focuses on controlling the robot mechanism in a realtime control loop, and therefore it only contains the components of a robot that are relevant in realtime: the robot joints (with encoders, transmisisons and actuators) and the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot.
The pr2_mechanism_model package is well tested and is released with a stable API.
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: ROS Orphaned Package Maintainers <ros-orphaned-packages AT googlegroups DOT com>
- Author: Eric Berger berger@willowgarage.com, Stuart Glaser, Wim Meeussen
- License: BSD
- Source: git https://github.com/pr2/pr2_mechanism.git (branch: melodic-devel)
Overview
The pr2_mechanism_model package contains the pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState C++ class, which is an interface to the robot joints and a description of the robot model. The RobotState gives easy access to individual joints. To work with a kinematic chain that contains multiple joints, pr2_mechanism_model contains a pr2_mechanism_model::Chain tool that represents a full kinematic chain and interfaces with the RobotState.
The following diagram shows how the mechanism model is set up on the robot and in simulation.
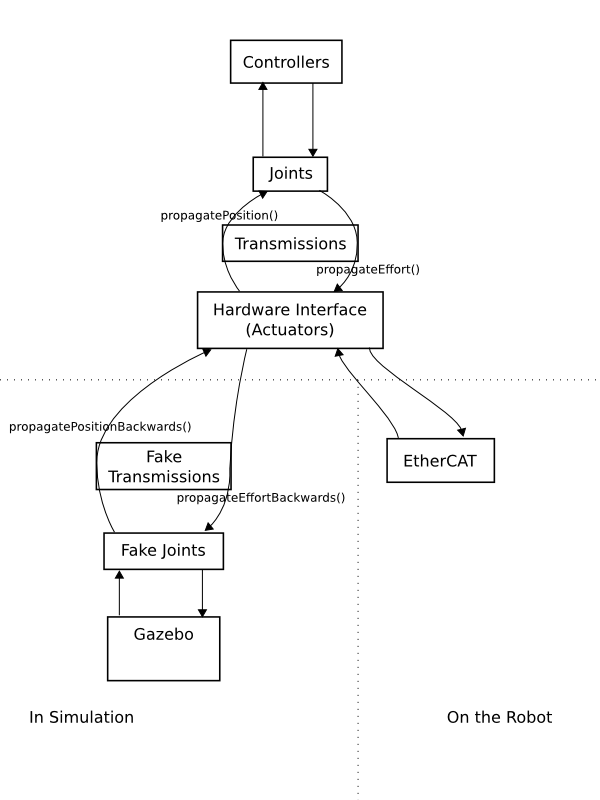
Components
pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState
pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState is the main class in this package. When a controller gets initialized, the controller manager passes the controller a pointer to the RobotState (see the controller interface). The robot state describes both the kinematic/dynamic model of the robot and the current state of the robot. The state of the robot is defined by the position/velocity/effort of the joints in the robot. The model of the robot is a urdf object, as defined in the urdf package. Additionally, the RobotState provides access to the 'controller time', the time at which a controller cycle is started. To see an example on how to use the RobotState, check out the controllers tutorials.
pr2_mechanism_model::JointState
The pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState provides access by name to all the pr2_mechanism_model::JointStates it contains. To get access to a JointState, use the following method:
JointState* js = robot_state_->getJointState(name);
From a JointState you can extract joint position, effort, velocity, and command the desired joint effort: To get e.g. the measured joint position from the JointState, use:
double position = js->position_;
or, to set the commanded effort on JointState, use:
js->commanded_effort_ = my_command;
The tutorials give more examples on how to use the JointState.
The JointState also gives access to the joint model, which contains things like the joint type, axis, reference position, etc. To e.g. get the joint type, use:
if (js->joint_->type == urdf::Joint::Continuous)
ROS_INFO("This is a continuous joint");The urdf API documentation provides all details.
For reference documentation, check out the code api. From a JointState you can read the measured position, measured velocity and measured effort effort, and write the commanded effort.
URDF Safety Controller Limits
Class member urdf::Joint::safety
js->joint_->safety
contains various parameters used to configure joint safety controller position and velocity limits. Please see the code api for more details.
Transmissions
The pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState also provides access to the transmissions between the motors and the joints. Typically you should not need the transmissions, unless you are using some advanced dynamic model, or you are calibrating the joints. To get access to a JointState, use the following method:
Transmission* tr = robot_state_->getTransmission(name);
See the code api for more details.
For details on the transmission description format, check out the transmission elements page.
Controller time
Every time a controller cycle is started, the controller manager records the time. This time can be accessed by all controllers through the pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState. When a controller e.g. needs to compute the duration between two consecutive update loops, it should use the controller time, not the system time. In contrast to the system time, the controller time is not affected by the time other controllers consume in their update loop. Moreover, the controller time is the best measure of when the communication with the hardware actually occurs. To get access to the controller time, use:
ros::Time time = robot_state_->getTime();
Robot model
The pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState contains a urdf robot description object. There is lots of documentation on the urdf model, and there are even a number of tutorials you could look at. To get access to the urdf model use:
urdf::Model m = robot_state_->robot_->robot_model_;
Chain
The pr2_mechanism_model::Chain class provides an easy way to work with a kinematic chain that consists of multiple joints. Instead of finding all the joints by iterating through the RobotState, the Chain will pull out all the joints between a given root and tip link:
pr2_mechanism_model::Chain chain; chain.init(robot_state, root_name, tip_name);
From a Chain you can get the positions/velocities/efforts of all the joints, and set the efforts of all joints:
KDL::JointArray jnt_pos; chain.getPositions(jnt_pos); KDL::JointArrayVel jnt_pos_vel; chain.getVelocities(jnt_pos_vel); KDL::JointArray jnt_eff; chain.getEfforts(jnt_eff); KDL::JointArray jnt_eff; chain.setEfforts(jnt_eff);
From a chain you can also extract a KDL::Chain:
KDL::Chain kdl_chain; chain.toKDK(kdl_chain);
See the code API for more details.
Usage Documentation
The pr2_mechanism_model is used when writing a realtime controller. For example code on how to use the pr2_mechanism_model::RobotState and the pr2_mechanism_model::JointState classes, check out this tutorial on writing a realtime joint controller. To see an example on how to use the pr2_mechanism_model::Chain object for Cartesian control, check out this tutorial on writing a realtime Cartesian controller.
